Upload and Retrieve Image on MongoDB using Mongoose
Prerequisites: For getting started with this you should have some familiarity with NodeJS, ExpressJS, MongoDB and Mongoose.
- NodeJS : It is a free open source server environment that uses JavaScript on the server and runs on various platform (Windows, Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, etc.).It uses asynchronous programming.
- ExpressJS : It is a NodeJS web application server framework, designed for building single-page, multi-page, and hybrid web applications. It is the de facto standard server framework for node.
- MongoDB : MongoDB is a NoSQL database.MongoDB is a JSON document datastore. It allows you to store and query JSON style documents with a few smarts on top.
- Mongoose : Mongoose is an Object Data Modeling (ODM) library for MongoDB and Node. js. It manages relationships between data, provides schema validation, and is used to translate between objects in code and the representation of those objects in MongoDB.
To start, install the required packages and modules:
Hey geek! The constant emerging technologies in the world of web development always keeps the excitement for this subject through the roof. But before you tackle the big projects, we suggest you start by learning the basics. Kickstart your web development journey by learning JS concepts with our JavaScript Course. Now at it's lowest price ever!
- ExpressJS allows us to set up middleware to respond to HTTP Requests.
npm install express --save
- The module "body-parser" enables reading (parsing) HTTP-POST data.
npm install body-parser --save
- Mongoose is a MongoDB client library providing object-modelling for use in an asynchronous environment. Mongoose supports both promises and callbacks.
npm install mongoose --save
- Multer is nodejs middleware used for uploading files.
npm install multer --save
- Dotenv is a zero-dependency module that loads environment variables from a .env file into process.env.
npm install dotenv --save
- EJS (Embedded Javascript) is a templating engine for nodejs. This engine helps to create an HTML pages via templates with minimal code.
npm install ejs --save
- nodemon is a developer tool that automatically restarts the node application when file changes in the code directory are detected. It improves the developer experience when working on node-based applications. Since this is a development tool and not part of our application code, we use `–save-dev` when installing this module:
npm install nodemon --save-dev
Now let's start coding! To upload an image and retrieve image by MongoDB using Mangoose, follow each of the steps below one by one.
- Step 0: Create the file ` .env ` that will contain environment-specific settings.
Javascript
MONGO_URL=mongodb:
PORT=3000
- Step 1: Create our server file ` app.js `. Add the following code to it:
Javascript
var express = require( 'express' )
var app = express()
var bodyParser = require( 'body-parser' );
var mongoose = require( 'mongoose' )
var fs = require( 'fs' );
var path = require( 'path' );
require( 'dotenv/config' );
- Step 2: Connect to MongoDB using the URL for your database. Here 'process.env.MONGO_URL' is used for the database URL. This value is retrieved from ` .env ` as an environment variable by the module `dotenv`. Add the following code to ` app.js `
Javascript
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URL,
{ useNewUrlParser: true , useUnifiedTopology: true }, err => {
console.log( 'connected' )
});
- Step 3: Once we have established a connection to our database and required all the necessary packages, we can now begin defining our server-side logic. So for storing an image in MongoDB, we need to create a schema with mongoose. For that create the file ` model.js ` file and define the schema. The important point here is that our data type for the image is a Buffer which allows us to store our image as data in the form of arrays.
Javascript
var mongoose = require( 'mongoose' );
var imageSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
desc: String,
img:
{
data: Buffer,
contentType: String
}
});
module.exports = new mongoose.model( 'Image' , imageSchema);
- Step 4: We want to set EJS as our templating engine with Express. EJS is specifically designed for building single-page, multi-page, and hybrid web applications. It has become the standard server framework for nodejs. The default behavior of EJS is that it looks into the ` views ` folder for the templates to render. We will create our templates in a later step.
Add the following code to ` app.js `:
Javascript
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }))
app.use(bodyParser.json())
app.set( "view engine" , "ejs" );
- Step 5: We will define the storage path for the image we are uploading. Here, we are using the middleware Multer to upload the photo to the server in a folder called ` uploads ` so we can process it.
Add the following code to ` app.js `:
Javascript
var multer = require( 'multer' );
var storage = multer.diskStorage({
destination: (req, file, cb) => {
cb( null , 'uploads' )
},
filename: (req, file, cb) => {
cb( null , file.fieldname + '-' + Date.now())
}
});
var upload = multer({ storage: storage });
- Step 6: Now, load the Image model by adding the following code to ` app.js `:
Javascript
var imgModel = require( './model' );
- Step 7: Set up the handler for the GET request to our server. The response displays an HTML page showing all the images stored in the database, and provides a UI for uploading new images.
Add the following code to ` app.js `:
Javascript
app.get( '/' , (req, res) => {
imgModel.find({}, (err, items) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
res.status(500).send( 'An error occurred' , err);
}
else {
res.render( 'imagesPage' , { items: items });
}
});
});
- Step 8: Handle the POST request that processes the form data submitted by the user from our HTML UI. This request will have the new images being uploaded.
Add the following code to ` app.js `:
Javascript
app.post( '/' , upload.single( 'image' ), (req, res, next) => {
var obj = {
name: req.body.name,
desc: req.body.desc,
img: {
data: fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname + '/uploads/' + req.file.filename)),
contentType: 'image/png'
}
}
imgModel.create(obj, (err, item) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
}
else {
res.redirect( '/' );
}
});
});
- Step 9: Configure the server to default port with the default of 3000 . The environment variable process.env.PORT is used if set in your ` .env `.
Add the following code to ` app.js `:
Javascript
var port = process.env.PORT || '3000 '
app.listen(port, err => {
if (err)
throw err
console.log(' Server listening on port', port)
})
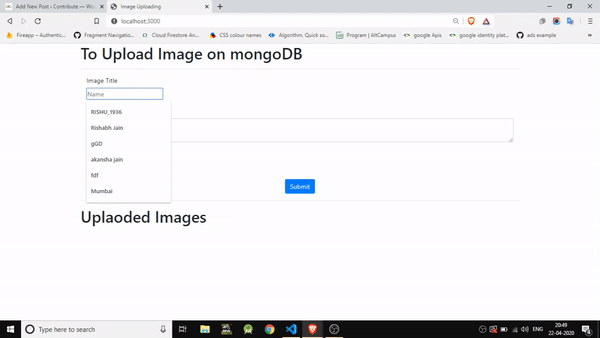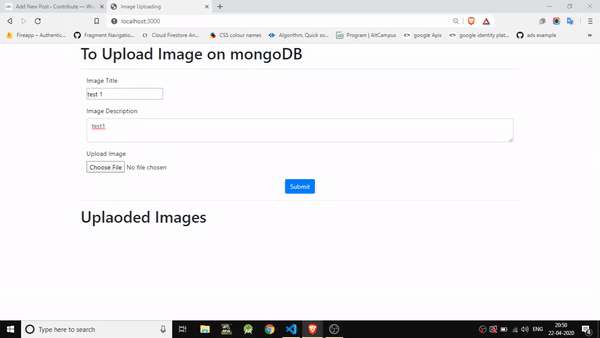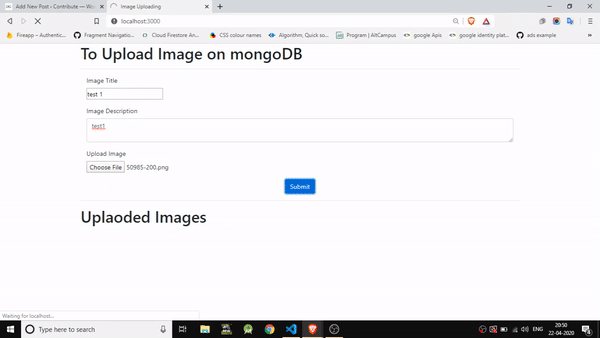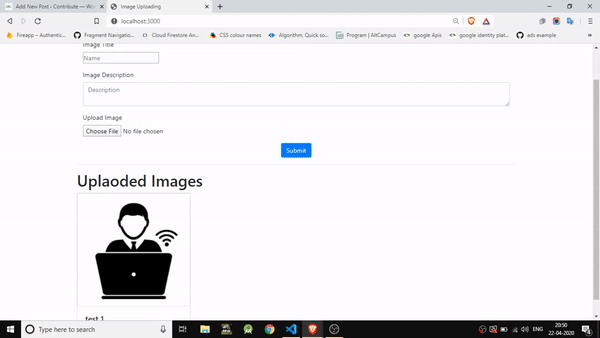
- Step 10: This is the HTML template for the "upload page". Notice that the src parameter for the <img> is not a typical URL. This format enables displaying the image stored in binary format in the Mongo database, and we convert it to base64 so that the browser can render it.
Add the following code to the ` views/imagesPage.ejs `:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
< html lang = "en" >
< head >
< meta charset = "UTF-8" >
< meta name = "viewport" content = "width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" >
< title >Image Uploading</ title >
</ head >
< body >
< h1 >To Upload Image on mongoDB</ h1 >
< hr >
< div >
< form action = "/" method = "POST" enctype = "multipart/form-data" >
< div >
< label for = "name" >Image Title</ label >
< input type = "text" id = "name" placeholder = "Name"
value = "" name = "name" required>
</ div >
< div >
< label for = "desc" >Image Description</ label >
< textarea id = "desc" name = "desc" value = "" rows = "2"
placeholder = "Description" required>
</ textarea >
</ div >
< div >
< label for = "image" >Upload Image</ label >
< input type = "file" id = "image"
name = "image" value = "" required>
</ div >
< div >
< button type = "submit" >Submit</ button >
</ div >
</ form >
</ div >
< hr >
< h1 >Uploaded Images</ h1 >
< div >
<% items.forEach(function(image) { %>
< div >
< div >
< img src="data:image/<%=image.img.contentType%>;base64,
<%=image.img.data.toString('base64')%>">
< div >
< h5 ><%= image.name %></ h5 >
< p ><%= image.desc %></ p >
</ div >
</ div >
</ div >
<% }) %>
</ div >
</ body >
</ html >
- Step 11: Create the directory ` uploads ` that will hold our uploaded images. The code in Step 8 refers to this directory.
- Step 12: Start the server by running the command: ` nodemon app.js `
Output Open your browser to http://localhost:3000/ . You should now see:
Congratulations! You did it!
Posted by: antwanantwanmeschkee0277785.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/upload-and-retrieve-image-on-mongodb-using-mongoose/